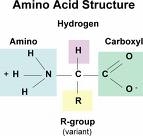
Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids.
The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. They are particularly important in biochemistry, where the term usually refers to alpha-amino acids.
Amino acids are critical to life, and have many functions in metabolism. One particularly important function is to serve as the building blocks of proteins, which are linear chains of amino acids. Amino acids can be linked together in varying sequences to form a vast variety of proteins.
Twenty-two amino acids are naturally incorporated into polypeptides and are called proteinogenic or standard amino acids. Of these, 20 are encoded by the universal genetic code. Nine standard amino acids are called "essential" for humans because they cannot be created from other compounds by the human body, and so must be taken in as food.
No comments:
Post a Comment